3D CT Angiography
3D technology provides detailed look at blood vessels.
What to expect
Less invasive procedure
Scan time takes under 1 minute
Entire process may take an hour
- A CTA is an outpatient procedure and less invasive.
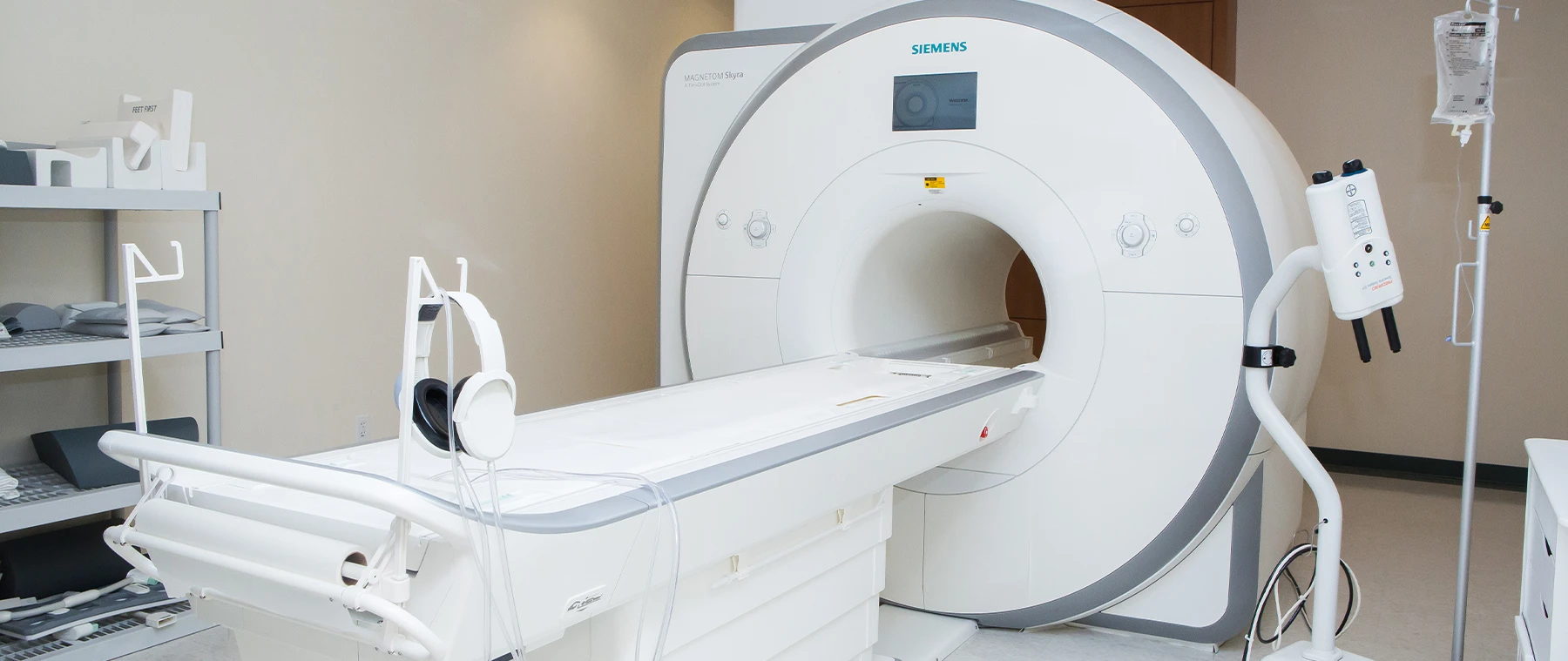
- You will lie on a table that passes through a doughnut-shaped opening in the scanner.
Outpatient Procedure is Less Invasive Than Traditional Test
A computed tomography angiogram (CT angiogram or CTA) is a test that uses sophisticated technology and software to provide images of the blood vessels that go to the heart, lung, brain, kidneys, head, neck, legs, and arms. At Main Street Radiology, CTA is most commonly used to study the aorta (the main artery leading to the heart) and blood vessels supplying the lungs and kidneys.
A CT angiogram can show narrowed or blocked areas of a blood vessel. It can also show any aneurysms (a bulge or weak spot) or a build-up of fatty material called plaque in a blood vessel.
- In the past, these conditions have been diagnosed with a traditional angiogram, which consists of placing a catheter - or tube - directly into the artery being studied.
- A CTA is less invasive. It requires only an iodine-based contrast dye to be injected into the arm.
- With the advent of multi-detector CT, faster scanners with higher resolution can capture detailed images of image smaller vessels, including the arteries of the brain and extremities.
- At Main Street Radiology, our 16-detector CT and advanced software generates 3D images of arteries that provide highly accurate assessments of a patient's blood vessels.
The CT Angiogram Procedure
A CTA is an outpatient procedure, which can show narrowed or blocked areas of a blood vessel. It can also show any aneurysms (a bulge or weak spot) or a build-up of fatty material called plaque in a blood vessel.
How Does It Work?
The patient lies on a table that passes through a doughnut-shaped opening in the scanner. Using an IV tube and needle, a special dye is put in a vein in your arm or hand to make the blood vessels easier to see on the scan.
Although the actual scanning portion of the test may take less than a minute, the entire process, including preparation, may take up to an hour.
Already Scheduled for A CT-Scan?
Already Scheduled for A CT-Scan?
Learn how to prep for your medical procedure.
Five convenient locations
Schedule an Appointment
Online
Fill out this form and we'll contact you as soon as possible. Please do not include any personal or financial information when using this form.
By Phone
Call or text to schedule an appointment. You may text us any required information (name, date of birth, and a picture of your prescription.) and a scheduling representative will be in touch.
- Call Us: (718) 428-1500
- Text Us: (929) 430-2761
HOURS
Monday-Friday: 8 a.m. to 8 p.m
Saturday: 8 a.m. to 4 p.m.
Sunday: 8 a.m. to 2 p.m. (Flushing Office Only)